Abstract
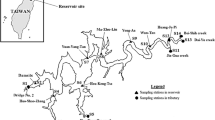
In this paper, we use an integrated approach to carry out a comprehensive evaluation of water quality in the Beni Haroun (BH) dam, the largest surface water resource in Algeria. Several techniques have been employed under the same framework, including the Canadian Council Ministers Environment Water Quality Index (CCME-WQI), principal component analysis and factor analysis (PCA/FA), the K-means clustering, and the ordinary least square (OLS) analysis. A data set of 22 physicochemical parameters has been collected, over a period of 11 years, from three sampling stations: Ain Smara (ST1) and Menia (ST2), both located upstream of “Wadi Rhumel,” and BH dam station (ST3), located at the dam site. The PCA/FA enables the identification of seven key factors that influence significantly BH dam water quality. The average values of CCME indices at the BH dam were 17, 40, 42, and 32 for drinking, irrigation, industry, and aquatic life purposes, respectively, which indicate poor water quality, according to the CCME categorization scheme. Besides, the K-means algorithm has been proven to be a very useful machine learning tool to detect that the major source of BH dam pollution is “Wadi Rhumel.” Finally, OLS analysis, along with the Mann-Kendall test, highlighted the positive trend of BH dam’s water quality.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AI:
-
artificial intelligence
- ALWQI:
-
aquatic life WQI
- ANOVA:
-
analysis of variance
- ANRH:
-
Agence Nationale des Resources Hydrauliques
- BCWQI:
-
British Columbia WQI
- BH:
-
Beni Haroun
- BOD:
-
biochemical oxygen demand
- CA:
-
cluster analysis
- CCME-WQI:
-
Canadian Council Ministers Environments WQI
- CEC:
-
Commission of European Committees
- COD:
-
chemical oxygen demand
- CWQI:
-
Canadian WQI
- DA:
-
discriminant analysis
- DO:
-
dissolved oxygen
- DWAF:
-
Department of Water Affairs and Forestry
- DWQI:
-
drinking WQI
- EC:
-
electrical conductivity
- FA:
-
factor analysis
- FAO:
-
Food and Agriculture Organization
- InWQI:
-
industrial WQI
- IWQI:
-
irrigation WQI
- KMO:
-
Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin
- NSF-WQI:
-
National Sanitation Foundation WQI
- OLS:
-
ordinary least square
- PCA:
-
principal component analysis
- PCs:
-
principal components
- pH:
-
power of hydrogen
- ST1:
-
Ain Smara station
- ST2:
-
Menia station
- ST3:
-
Grarem station
- T:
-
water temperature
- TSS:
-
total suspended solid
- VFs:
-
Varifactors
- WE:
-
Wadi Endja
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- WQI:
-
Water Quality Index
- WR:
-
Wadi Rhumel
References
Abbasi, T., & Abbasi, S. A. (2012). Water quality indices. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Areerachakul, S., & Sanguansintukul, S. (2010). Clustering analysis of water quality for canals in Bangkok, Thailand. In D. Taniar, O. Gervasi, B. Murgante, E. Pardede, & B. O. Apduhan (Eds.), International Conference of Computational Science and Its Applications – ICCSA 2010, Fukuoka, Japan, March 23–26, 2010, Proceedings (Vol. 2010, pp. 215–227). Springer Heidelberg.
Ay, M., & Kisi, O. (2014). Modelling of chemical oxygen demand by using ANNs, ANFIS and k-means clustering techniques. Journal of Hydrology, 511, 279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.01.054.
Benahmed, L., & Houichi, L. (2018). The effect of simple imputations based on four variants of PCA methods on the quantiles of annual rainfall data. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 190, 569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6913-y.
Bouaroudj, S., Menad, A., Bounamous, A., Ali-Khodja, H., Gherib, A., Weigel, D. E., & Chenchouni, H. (2019). Assessment of water quality at the largest dam in Algeria (Beni Haroun Dam) and effects of irrigation on soil characteristics of agricultural lands. Chemosphere, 219, 76–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.193.
Bouguerne, A., Boudoukha, A., Benkhaled, A., & Mebarkia, A.-H. (2017). Assessment of surface water quality of Ain Zada dam (Algeria) using multivariate statistical techniques. International Journal of River Basin Management, 15, 133–143. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2016.1215325.
Brown, R. M., McClelland, N. I., Deininger, R. A., Tozer, R. G. (1970). A Water Quality Index- do were dare.
Canadian Council Ministers of Environment (CCME). (2001). Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: CCME Water Quality Index 1.0, User’s manual, Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines (p. 5). Winnipeg: Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment.
Commission of European Committees (CEC) (1978). Council Directive of 18 July 1978 on the quality of fresh waters needing protection or improvement in order to support fish life, (78/659/EEC). Official J L/222:1–10.
Davies, D. L., & Bouldin, D. W. (1979). A cluster separation measure. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, PAMI-1, 224–227. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.1979.4766909.
Department of Water Affairs and Forestry (DWAF) (1996). South African Water Quality Guidelines, 2nd ed., Industrial Use, vol. 3. Department of Water Affairs and Forestry, Pretoria, South Africa.
Dinius, S. H. (1972). Social accounting system for evaluating water resources. Water Resources Research, 8, 1159–1177. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR008i005p01159.
Djeddi, H., Kherief Nacereddine, S., Keddari, D., & Afri-Mehennaoui, F.-Z. (2018). Content of trace metallic elements Cu, Zn and Pb sediments of the Béni Haroun Dam (North-East Algeria). European Scientific Journal, ESJ, 14, 269. https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2018.v14n15p269 (in French).
Djelita, B., Bouzid-Lagha, S., & NEHAR, K. C. (2016). Spatial and temporal patterns of the water quality in the Hammam Boughrara Reservoir in Algeria. In P. Grammelis (Ed.), Energy, Transportation and Global Warming (pp. 635–653). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Dunn, J. C. (1974). Well-Separated Clusters and Optimal Fuzzy Partitions. Journal of Cybernetics, 4, 95–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/01969727408546059.
Farzadkia, M., Djahed, B., Shahsavani, E., & Poureshg, Y. (2015). Spatio-temporal evaluation of Yamchi Dam basin water quality using Canadian Water Quality Index. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 187, 168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4379-8.
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (1994). Water quality for agriculture. 29 Rev. 1. pp. 174.
González, S. O., Almeida, C. A., Calderón, M., Mallea, M. A., & González, P. (2014). Assessment of the water self-purification capacity on a river affected by organic pollution: Application of chemometrics in spatial and temporal variations. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 10583–10593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3098-y.
Hafsi, R., Ouerdachi, L., Kriker, A. E. O., & Boutaghane, H. (2016). Assessment of urbanization/impervious effects on water quality in the urban river Annaba (Eastern Algeria) using physicochemical parameters. Water Science and Technology, 74, 2051–2059. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.350.
Hamil, S., Arab, S., Chaffai, A., Baha, M., & Arab, A. (2018). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical analysis techniques: A case study from Ghrib dam, Algeria. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 754.
Hamlat, A., Tidjani, A. E.-B., Yebdri, D., Errih, M., & Guidoum, A. (2013). Water quality analysis of reservoirs within Western Algeria catchment areas using Water Quality Index CCME WQI. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology—AQUA, 63, 311–324.
Hamlat, A., Guidoum, A., & Koulala, I. (2016). Status and trends of water quality in the Tafna catchment: A comparative study using water quality indices. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination, 7, 228–245. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2016.155.
Hartigan, J. A., & Wong, M. A. (1979). Algorithm AS 136: A k-means clustering algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series C (Applied Statistics), 28, 100–108.
Heddam, S., Lamda, H., & Filali, S. (2016). Predicting effluent biochemical oxygen demand in a wastewater treatment plant using generalized regression neural network based approach: A comparative study. Environmental Processes, 3, 153–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0129-3.
Helena, B., Pardo, R., Vega, M., Barrado, E., Fernandez, J. M., & Fernandez, L. (2000). Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Research, 34, 807–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00225-0.
Horton, R. K. (1965). An index number system for rating water quality. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation, 37, 300–306.
Javadi, S., Hashemy, S. M., Mohammadi, K., Howard, K. W. F., & Neshat, A. (2017). Classification of aquifer vulnerability using K-means cluster analysis. Journal of Hydrology, 549, 27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.03.060.
Kateb, Z., Bouchelkia, H., Benmansour, A., & Belarbi, F. (2020). Sediment transport modeling by the SWAT model using two scenarios in the watershed of Beni Haroun dam in Algeria. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13, 653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05623-0.
Kaufman, L., & Rousseeuw, P. J. (1990). Finding groups in data: An introduction to cluster analysis (Vol. 725). Hoboken: Wiley Inc.
Kendall, M. (1975). Rank Correlation Methods. Charles Griffin, 202, 15.
Kherief Nacereddine, S., Djeddi, H., Benayache, N. Y., & Afri-Mehennaoui, F. Z. (2018). Nutrient and phytoplankton dynamics in the Beni Haroun dam in Eastern Algeria. European Scientific Journal, ESJ, 14, 111. https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2018.v14n12p111 (in French).
Kükrer, S., & Mutlu, E. (2019). Assessment of surface water quality using Water Quality Index and multivariate statistical analyses in Saraydüzü Dam Lake, Turkey. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 191, 71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7197-6.
Ledesma, M. M., Bonancea, M., Ledesma, C. R., Rodríguez, M. C., & Pinotti, L. (2018). Water quality assessment of the Cassaffousth Reservoir using multivariate statistical techniques. Ab Intus, 1, 27–38.
Liu, C.-W., Lin, K.-H., & Kuo, Y.-M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of The Total Environment, 313, 77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00683-6.
Lumb, A., Halliwell, D., & Sharma, T. (2006). Application of CCME Water Quality Index to monitor water quality: A case study of the Mackenzie River Basin, Canada. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 113, 411–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9092-6.
MacQueen, J. (1967). Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations (pp. 281–297). Oakland: Proceedings of the fifth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability.
Mann, H. B. (1945). Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica, 13, 245–259. https://doi.org/10.2307/1907187.
Marouf, N. (2012). Study of water quality and sediment transport in the Beni-Haroun dam (MILA): Its impact on the environment of the region. Biskra: Mohamed Khider University 242 pp, (in French).
Marouf, N., & Remini, B. (2016). Study of Beni Haroun dam pollution (Algeria). Desalination and Water Treatment, 57, 2766–2774. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.982192.
Matta, G., Kumar, A., Naik, P. K., Tiwari, A., & Berndtsson, R. (2018a). Ecological analysis of nutrient dynamics and phytoplankton assemblage in the Ganga River System, Uttarakhand. Taiwan Water Conservancy, 66, 1–12.
Matta, G., Naik, P. K., Machell, J., Kumar, A., Gjyli, L., Tiwari, A. K., & Kumar, A. (2018b). Comparative study on seasonal variation in hydro-chemical parameters of Ganga River water using comprehensive pollution index (CPI) at Rishikesh (Uttarakhand) India. Desalination and Water Treatment, 118, 87–95. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.22487.
Matta, G., Kumar, A., Tiwari, A. K., Naik, P. K., & Berndtsson, R. (2020). HPI appraisal of concentrations of heavy metals in dynamic and static flow of Ganga River System. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22, 33–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-018-0182-3.
Mebarki, A. (2000). Low water flows, effluents and protection of water resources in the Mediterranean basins of eastern Algeria (in French). Geocarrefour Revue de Geogaphie de Lyon (France).
Mebarki, A. (2005). Hydrology of the Algerian Eastern basins: Water resources, development and environment. Algeria: University of Constantine 360 pp, (in French).
Mebarki, A., Benabbas, C., & Grecu, F. (2008). “Beni-Haroun” (Oued Kébir-Rhumel, Algeria) system: Hydraulic developments and morpho-geological constraints (in French). Analele Universitatii Bucuresti: Geografie, 57, 37–51.
Moskowitz, C. (2008). What makes earth special compared to other planets? online: https://www.space.com/5595-earth-special-compared-planets.html. Accessed 16 April 2020.
Müller, B., Berg, M., Yao, Z. P., Zhang, X. F., Wang, D., & Pfluger, A. (2008). How polluted is the Yangtze river? Water quality downstream from the Three Gorges Dam. Science of The Total Environment, 402, 232–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.04.049.
Official Journal of the Algerian Republic (OJAR) (2011). The guidelines for Algerian drinking water quality. Off. J. Algerian Rep. 34, 17 Rajab 1432, 19 June 2011.
Remini, B., Toumi, A. (2017). The Beni Haroun reservoir (Algeria) is it threatened by siltation? LARHYSS Journal P-ISSN 1112-3680/E-ISSN 2521-9782, 249-263.
Rodier, J., Legube, B., Merlet, N. (2009). Water analysis (In French).
RStudio Team. (2019). RStudio: Integrated development for R. Boston: RStudio, Inc..
Samiotis, G., Trikoilidou, E., Tsikritzis, L., & Amanatidou, E. (2018). Comparative water quality assessment between a young and a stabilized hydroelectric reservoir in Aliakmon River, Greece. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 190, 234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6602-x.
Shi, W., & Zeng, W. (2014). Application of k-means clustering to environmental risk zoning of the chemical industrial area. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 8, 117–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-013-0581-5.
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environmental Modelling & Software, 22, 464–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2006.02.001.
Shrestha, S., Kazama, F., & Nakamura, T. (2008). Use of principal component analysis, factor analysis and discriminant analysis to evaluate spatial and temporal variations in water quality of the Mekong River. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 10, 43–56. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2008.008.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., Mohan, D., & Sinha, S. (2004). Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—a case study. Water Research, 38, 3980–3992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.06.011.
Smith, D. G. (1990). A better water quality indexing system for rivers and streams. Water Research, 24, 1237–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(90)90047-A.
Stoner, J. D. (1978). Water-quality indices for specific water uses. Department of the Interior, Geological Survey.
Terrado, M., Barceló, D., Tauler, R., Borrell, E., & Sd, C. (2010). Surface-water-quality indices for the analysis of data generated by automated sampling networks. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 29, 40–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2009.10.001.
Tibshirani, R., Walther, G., & Hastie, T. (2001). Estimating the number of clusters in a data set via the gap statistic. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology), 63, 411–423.
Tiri, A., Belkhiri, L., & Mouni, L. (2018). Evaluation of surface water quality for drinking purposes using fuzzy inference system. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 6, 235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.01.006.
Tukey, J. W. (1977). Exploratory data analysis. Reading: Addison-Wesley.
Varol, M., & Şen, B. (2008). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of Behrimaz Stream, Turkey. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 159, 543–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0650-6.
Varol, M., Gökot, B., Bekleyen, A., & Şen, B. (2012). Spatial and temporal variations in surface water quality of the dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin, Turkey. Catena, 92, 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.013.
Wang, X., Cai, Q., Ye, L., & Qu, X. (2012). Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in stream water quality by multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Xiangxi River basin, China. Quaternary International, 282, 137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2012.05.015.
Weatherill, G., & Burton, P. W. (2009). Delineation of shallow seismic source zones using K-means cluster analysis, with application to the Aegean region. Geophysical Journal International, 176, 565–588.
Wei, G., Yang, Z., Cui, B., Li, B., Chen, H., Bai, J., & Dong, S. (2009). Impact of dam construction on water quality and water self-purification capacity of the Lancang River, China. Water Resources Management, 23, 1763–1780.
World Health Organization (WHO) (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality, vol. 1, 540 pp.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2008). Guidelines for drinking water quality, Recommendations (Vol. 1). Geneva: WHO.
Zarei, H., & Pourreza Bilondi, M. (2013). Factor analysis of chemical composition in the Karoon River basin, southwest of Iran. Applied Water Science, 3, 753–761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0123-0.
Zotou, I., Tsihrintzis, V. A., & Gikas, G. D. (2019). Performance of seven Water Quality Indices (WQIs) in a Mediterranean River. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 191, 505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7652-4.
Zou, H., Zou, Z., & Wang, X. (2015). An enhanced K-means algorithm for water quality analysis of the Haihe River in China. International journal of environmental research and public health, 12, 14400–14413.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Agence Nationale des Resources Hydrauliques (ANRH) for their assistance in providing the necessary data. They also are grateful to Professor Abderrahmane BOUDOUKHA of the University of Batna, Algeria, for his pertinent information and valuable advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soltani, A.A., Bermad, A., Boutaghane, H. et al. An integrated approach for assessing surface water quality: Case of Beni Haroun dam (Northeast Algeria). Environ Monit Assess 192, 630 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08572-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08572-z