Key points
- Predator-prey cycles show the natural rise and fall of numbers of predators and prey over time.
- All organisms in a food web depend upon each other and changes to one can affect the others.
Predators and prey
Predators have adaptations which help them catch prey, such as exceptionally good hearing.
Prey also have adaptations which enable it to escape, such as good eyesight. A predator-prey graph shows the numbers of predators and prey in an ecosystem over time.
More predators will kill more prey. So the levels of prey reduce. This means less food for the predators. So some of them die, reducing the population. In turn, fewer predators means more prey can now survive. So their numbers gradually increase. And now that there is more food again, more predators survive and their numbers increase again.
All predators and prey exist on planet Earth in this same ongoing cycle.
Can you answer these questions based on the video?
1. What adaptation does the fox have?
2. What is the graph of predators and prey called?
Exceptionally good hearing.
A predator-prey cycle.
Animals that are hunted and eaten are prey, and these are consumed by predators. The final consumer at the top of the food chainA list of organisms in a habitat that shows feeding relationships and the energy which transfers from one to the next when consumed. is called a top (or apex) predator and is not eaten by anything else.
Over time the numbers of predators and prey in an ecosystem rises and falls in a predator-prey cycleA graph showing the natural rise and fall of numbers of predators and prey in a habitat.. As the number of prey increases, so does the number of predators shortly afterwards. This is because there is more food. This reduces the number of prey because they are hunted. Which reduces the number of predators because there is less food. This increases the number of prey and the cycle repeats.
Adaptations of predators and prey
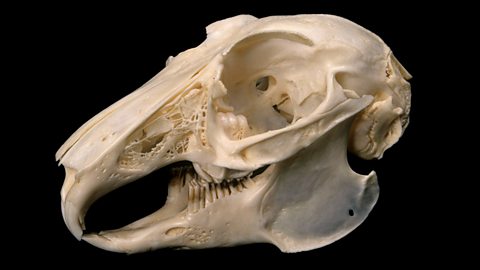
Prey have adaptationA characteristic that helps an organism to survive in its environment. to avoid being hunted, such as good hearing or eyes on the sides of their heads for a wide field of vision. This means it’s easier for them to see predators coming. Prey often have very good camouflage to avoid being seen.

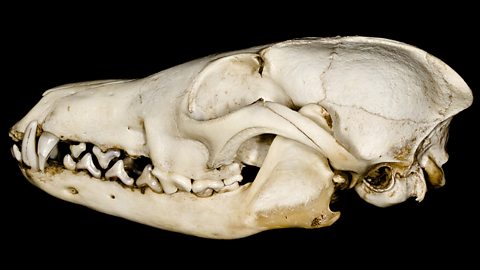
Predators have adaptations to hunt effectively like sharp claws and teeth, with eyes at the front of their heads to judge distances well. Some predators, for example cheetahs, can run very fast for short distances. Wolves can run great distances over longer periods of time, until their prey run out of energy.

Interdependence
All organisms in a food web depend upon each other. This is interdependence. If one organism increases or decreases its numbers dramatically, this has consequences for others.
Use the food web to answer the following questions:
1. What happens if the grass dies?
2. What happens if the population of slugs decreased?
3. What happens if the population of insects decreased?
The grass is the producer. If it died, the consumers that feed on it - rabbits, insects and slugs - would have no food. They would starve and die unless they could move to another habitat. All the other animals in the food web would die too because their food supplies would have gone. The populations of the consumers would fall as the population of the producer fell.
Slugs, rabbits and insects all eat grass. If there were fewer slugs there would be more grass for the rabbits and insects to eat. With more food, the populations of rabbits and insects would increase. However, the thrushes would have to eat more insects to maintain their population, so it is also possible that the population of insects could decrease. This may reduce the populations of voles and frogs.
There would be more food for the rabbits and slugs so their populations would increase. However, there would be less food for the frogs and voles, so their populations would decrease. This means less food for the foxes and hawks. However, there are likely to be more rabbits and thrushes for them to eat, so their populations might stay the same.
Food webs are able to flex and quickly bounce back to small changes in numbers. However big changes are more difficult for food webs to stabilise. These large changes are often due to human activity, such as deforestationThe cutting down of trees., constructing roads and buildings, and the use of chemical pesticidesChemicals used to kill pests..
Food security
All the food we eat relies on plants. This includes meat because animals such as pigs, sheep and cattle eat plants. Grasses such as wheat, barley and rice use the wind for pollinationThe fertilisation of flowers by the transfer of pollen from one to another.. Plants that produce fruit rely on insects and other animals for their pollination.
If the population of pollinating insects goes down, it reduces the amount of these plants for us to eat, and also the number of seeds for new plants to grow. Food security means having a reliable source of nutritious food.

Test your knowledge
Quiz
Test questions
Describe the stages in a predator-prey cycle.
As the number of prey increases, so does the predators shortly afterwards because there is more food.
This reduces the number of prey because they are hunted.
This reduces the number of predators because there is less food.
This increases the number of prey and the cycle repeats.
Working safely in the lab
Find out how to spot risks, hazards and understand hazard symbols

More on Ecosystems and habitats
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 7

- count4 of 7

- count5 of 7

- count6 of 7
