Hindustan Aeronautics Limited Airplanes and Aircrafts
- Photo: Metaweb (FB) / CC-BY-SA-2.5
HAL Ajeet
The HAL Ajeet was a development of the British Folland Gnat fighter that was built under licence in India by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited. - Photo: Metaweb (FB) / Public domainThe Hawker Siddeley HS 748 is a medium-sized turboprop airliner originally designed by the British firm Avro in the late 1950s as a replacement for the aging DC-3s then in widespread service as feederliners. Avro concentrated on performance, notably for STOL operations, and found a dedicated market. 380 aircraft were built by Hawker Siddeley. A larger, stretched development of the HS 748, the BAe ATP, attempted to compete with the de Havilland Canada Dash 8 but saw a limited production run.
HAL Basant
The Hindustan Aeronautics HA-31 Basant is a 1970s Indian agricultural monoplane built by Hindustan Aeronautics. Hindustan Aeronautics started to design an agricultural aircraft in 1968 designated the HAL-31 Mk 1 with a cockpit directly over the wing leading edge. It was re-designed as the HA-31 Mk II Basant and first flew on the 30 March 1972. The Basant is a conventional braced low-wing monoplane with a fixed tailwheel landing gear and powered by a 400 hp Avco Lycoming IO-720 piston engine. It had a raised cockpit to give the pilot a good all-round view during spraying operations. Production ended in 1980 after 39 aircraft had been built.- Photo: Metaweb (FB) / Public domainThe HAL Dhruv is a utility helicopter developed and manufactured by India's Hindustan Aeronautics Limited. The development of the Dhruv was first announced in November 1984, and it was subsequently designed with assistance from MBB in Germany. The helicopter first flew in 1992; however, its development was prolonged due to multiple factors including the Indian Army's requirement for design changes, budget restrictions, and sanctions placed on India following the 1998 Pokhran-II nuclear tests. The Dhruv entered service in 2002. It is designed to meet the requirement of both military and civil operators, with military variants of the helicopter being developed for the Indian Armed Forces, while a variant for civilian/commercial use has also been developed. The helicopter was first exported to Nepal and Israel. It is also on order with several other countries for both military and commercial uses. Military versions in production include transport, utility, reconnaissance and medical evacuation variants.
- The Hindustan Aeronautics HF-24 Marut was an Indian fighter-bomber aircraft of the 1960s. It was India's first jet aircraft, took first flight on 17 June 1961.
- The HAL HJT-36 Sitara is a subsonic intermediate jet trainer aircraft developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited for the Indian Air Force and the Indian Navy. The HJT-36 will replace the HAL HJT-16 Kiran as the Stage-2 trainer for the two forces. The Sitara is a conventional jet trainer with low swept wings, tandem cockpit and small air intakes for the engine on either side of its fuselage. It entered limited series production by 2010, final operational clearance was expected by the end-2014.
- Photo: Metaweb (FB) / CC-BY-SA-2.5
HAL HPT-32 Deepak
The HAL HPT-32 Deepak is an Indian prop-driven primary trainer manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited. The student and the instructor sit side-by-side. The aircraft can accommodate one passenger. HAL HT-2
The Hindustan HT-2 is an Indian two-seat primary trainer designed and built by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited. The HT-2 was the first company design to enter production in 1953 for the Indian Air Force and Navy, where it replaced the de Havilland Tiger Moth. The HT-2 is a low-wing cantilever monoplane with a fixed tailwheel landing gear. Powered by a 155hp Cirrus Major III piston engine the aircraft has enclosed tandem cockpits with dual controls. Apart from military use the aircraft was also used by Indian flying schools.- Photo: Metaweb (FB) / CC-BY
HAL Kiran
The HAL HJT-16 Kiran is an Indian two-seat intermediate jet trainer built by Hindustan Aeronautics. Used by the Indian Air Force for intermediate training for pilots trained on the HPT-32 Deepak. It is used by the Indian Air Force aerobatic team Surya Kiran and Indian naval aerobatic team Sagar Pawans. - Photo: Metaweb (FB) / CC-BY
HAL Light Combat Helicopter
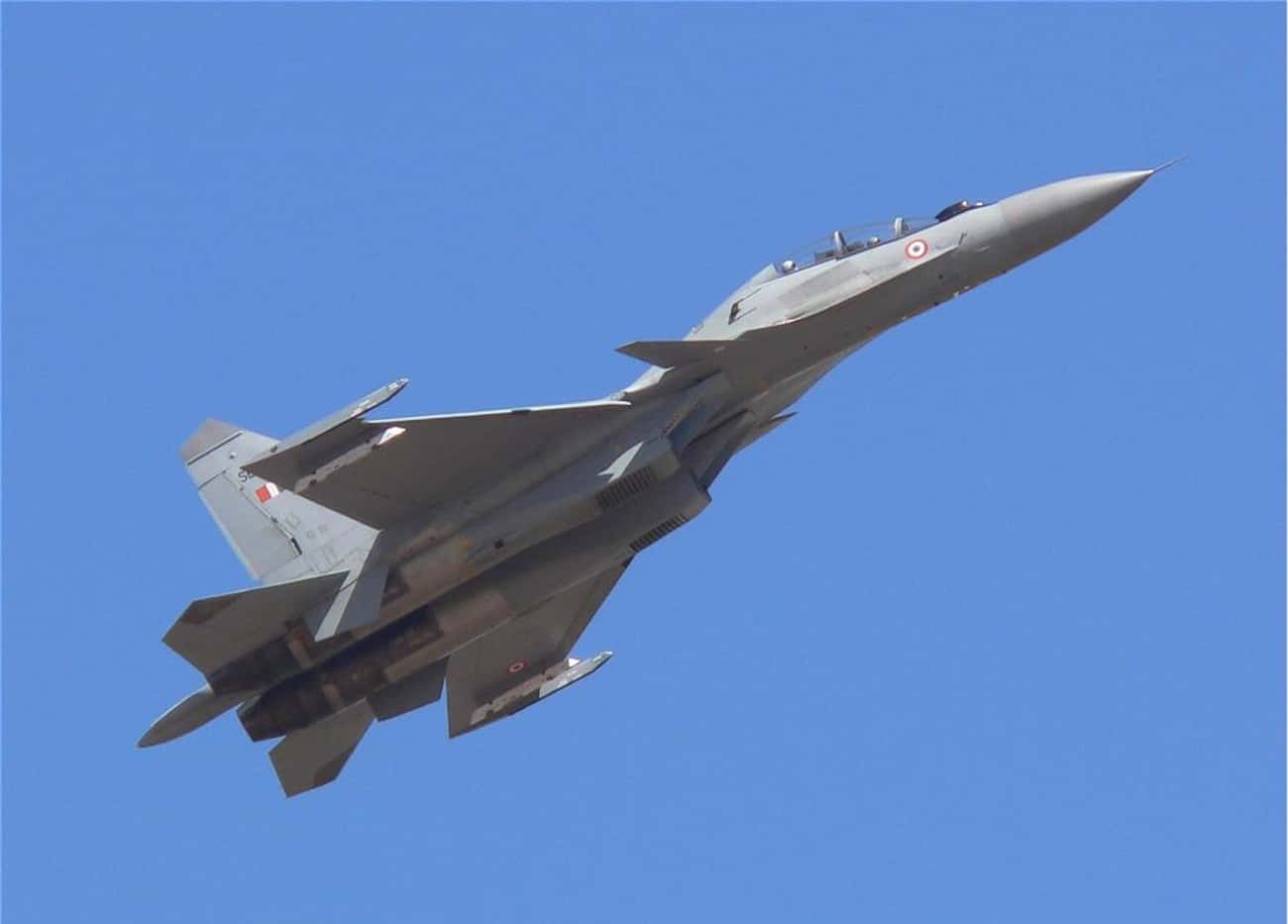
The HAL Light Combat Helicopter is a multirole combat helicopter being developed in India by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited for use by the Indian Air Force and the Indian Army. - Photo: Metaweb (FB) / Public domainThe Sukhoi Su-30MKI is a super-manoeuvrable twinjet air superiority fighter developed by Russia's Sukhoi and built under licence by India's Hindustan Aeronautics Limited for the Indian Air Force. A variant of the Sukhoi Su-30, it is a heavy, all-weather, long-range fighter. Development of the variant started after India signed a deal with Russia in 2000 to manufacture 140 Su-30 fighter jets. The first Russian-made Su-30MKI variant was accepted into the Indian Air Force in 2002, while the first indigenously assembled Su-30MKI entered service with the IAF in 2004. Additional MKIs have been ordered to increase the total to 272. The IAF had 200 Su-30MKIs in service as of August 2014. The Su-30MKI is expected to form the backbone of the Indian Air Force's fighter fleet to 2020 and beyond. The aircraft is tailor-made for Indian specifications and integrates Indian systems and avionics as well as French and Israeli sub-systems. It has abilities similar to the Sukhoi Su-35 with which it shares many features and components.
- Photo: Metaweb (FB) / CC-BY
HAL Light Observation Helicopter
The HAL Light Utility Helicopter is a single-engine light helicopter under development by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited of India. The 3-tonne helicopter for the Indian Army and the Indian Air Force will replace the fleet of Cheetah and Chetak helicopters. The project is in preliminary stages. The Indian military have a requirement for 384 helicopters of which 187 helicopters will be built by HAL. The first flight is expected in 2013. Production is planned to begin in 2015 at 10 per year, later on going up to 36 per year and delivery of 187 HAL’s LUHs is to be completed by 2022. As of 3 November 2012, the bottom structure assembly of the LUH ground test vehicle is complete and has been taken down from the jig last month. According to HAL, "LUH assembly jigs are modular and gaugeless jigs, concurrently designed along with structure design using 3D CAD. There are five assembly jigs and a coupling jig enabling modular and concurrent build- up of the structure. The jigs are built and validated using state-of-the-art CAMS-Computer Aided Measurement System to establish high accuracy and stability. - Photo: Metaweb (FB) / CC-BY-SA
HAL Pushpak
The Hindustan HUL-26 Pushpak was a 1950s Indian two-seat cabin monoplane designed and built by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, based on the Aeronca Chief. The Pushpak was a high-wing braced monoplane with a fixed tailwheel landing gear. The fuselage was built from metal tubing, the wing a aluminum ribs on a wooden spar, all covered in fabric. The Pushpak first flew on 28 September 1958 and was powered by a 90 hp Continental flat-four engine. Around 160 aircraft were produced for Indian flying clubs for use as basic trainers. - Photo: Metaweb (FB) / Public domainThe HAL Tejas is an Indian single-seat, single-jet engine, multi-role light fighter developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited. It is a tailless, compound delta wing design powered by a single engine. It came from the Light Combat Aircraft programme, which began in the 1980s to replace India's ageing MiG-21 fighters. Later, the LCA was officially named "Tejas", meaning "Radiance" by the then Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee. Tejas has a pure double delta wing configuration, with no tailplanes or canard, and a single dorsal fin. It integrates technologies such as relaxed static stability, fly-by-wire flight control system, multi-mode radar, integrated digital avionics system, composite material structures, and a flat rated engine. It is supersonic and highly manoeuvrable, and is the smallest and lightest in its class of contemporary combat aircraft. The Tejas is the second supersonic fighter developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited after the HAL HF-24 Marut. The Indian Air Force was reported to have a requirement for 200 single-seat and 20 two-seat conversion trainers, while the Indian Navy might order up to 40 single-seaters to replace its Sea Harrier FRS.51 and Harrier T.60.
Harlow PC-5
The Harlow PC-5 was a 1930s American military trainer version of the PJC-2 designed and built by the Harlow Aircraft Company.- The HAL Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft is an Indian proposal for a fifth-generation fighter aircraft being developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited and designed by India's Aeronautical Development Agency. It is a single-seat, twin-engine, stealth supermaneuverable all weather multirole fighter aircraft. Unofficial design work on the AMCA started in 2008 with official work started in 2011 and completed in 2014. In 2008 Indian Navy joined the programme for the naval variant optimized for the aircraft carriers operation. Amca's design and configuration is to be finalized in early 2015 before going to the Indian government for approval in late 2015. The first flight is scheduled to occur in 2023. It is a multirole combat aircraft designed for the air superiority, ground attack, bombing, intercepting and other types of roles. It combines supercruise, stealth, AESA radar, maneuverability, and advanced avionics to overcome and suppress previous generation fighter aircraft along with many ground and maritime defences. It will complement HAL Tejas, Sukhoi/HAL FGFA, the Su-30MKI and Rafale in the air force service and HAL Naval Tejas and Mikoyan MiG-29K in the naval service.
- Photo: Metaweb (FB) / CC-BY-SA
NAL Saras
The NAL Saras is the first Indian multi-purpose civilian aircraft in the Light Transport Aircraft category designed by the National Aerospace Laboratories.