

What is a primary consumer in a food chain? What is a producer? What are predators and prey? We answer all these questions and more!
A food chain is a sequence describing how different animals eat each other, showing the order in which living things depend on each other for food. Starting with a plant and ending with an animal, a food chain is a diagram showing how energy is transferred between different organisms in an ecosystem. Organisms include both plants and animals.
Eating food is how we get our energy. Without consuming calories and nutrition, we could not survive. The food chain shows how living things get their food. Some animals will only feed on plants, while others will eat other animals.
There are four different categories of organisms in the food chain: producers, consumers, prey and predators.
When multiple food chains combine together, this can be displayed in a diagram called a food web.

Primary consumers are organisms that eat the producers. Producers are at the top of the food chain. These are always plants, like grass. Plants get their energy from the sun by making their own food in a process called photosynthesis. Primary consumers are herbivores, which means that they are creatures that eat only plants.
Here are some examples of primary consumers:
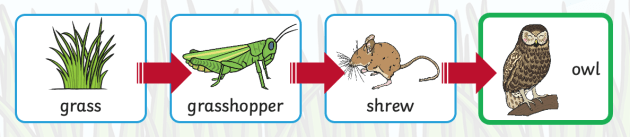
Above the producer is the consumer and above the consumer is the prey, followed by the predator. The prey eats the consumer, then the predator eats the prey.
Prey can be herbivores (creatures that eat only plants) or carnivores (creatures that mainly eat meat) or omnivores (animals that eat both plants and meats). Depending on the food chain, any of these might be the last one on the top. Most of the time, the animal at the top of the food chain is a predator who eats meat, either as a carnivore or an omnivore. The predator at the very top of the food chain, that nothing else eats, is called an apex predator.
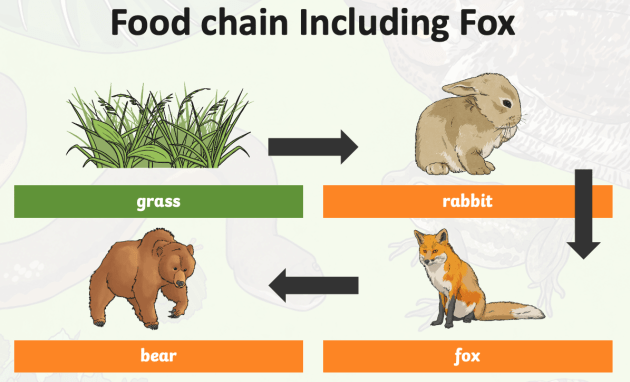
There are many different examples of food chains from different ecosystems. Here is an example of a food chain where grass is the producer, rabbits are the primary consumer, foxes are the prey and bears are the predators.
Another example of a food chain is:
In the above example, the plant is at the bottom of the food chain as the producer. The caterpillar consumes the plant. The caterpillar is then eaten by the mouse before the mouse finally becomes the prey of the predator: the wolf.
1. Apex predator (noun)
A species at the top of the food chain, with no predators of its own. Also called an alpha predator or top predator
2. Autotroph (noun)
An organism that can produce its own food and nutrients from chemicals in the atmosphere, usually through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
3. Bacteria (plural noun)
Single-celled organisms found in every ecosystem on Earth.
4. Carbon dioxide (noun)
A greenhouse gas produced by animals during respiration and used by plants during photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide is also the by-product of burning fossil fuels.
5. Ecosystem (noun)
The community and interactions of living and non-living things in an area.
 Home
Home  Membership
Membership  Customer Support
Customer Support  Create
Create  Blog
Blog 




















